disadvantages of enzymatic gravimetric method|Dietary fibre in foods: a review : importing The main analytical problems which have been shown to influence the performance of the enzymatic-gravimetric AOAC procedures are: variable starch removal, too high final .
webUma equipa de elite do FBI captura perigosos criminosos.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBr/BrasiIeirasGostosas. sub dedicado a todas gostosas do Brasil, seja ela famosa ou não! 🇧🇷. MembersOnline. •. historiamorta. ADMIN MOD. catarina paolino. TikToker.
Since 1989, total dietary fiber values in USDA databases were determined by the enzymatic-gravimetric (EGF) method (AOAC 991.43), where “fiber” is the residue remaining .
Enzymatic-gravimetric methods. In the early 1980s, a enzymatic-gravimetric method was developed in which the sum of soluble and insoluble polysaccharides and lignin were .Dietary fibre can be determined by different methods, mainly by: enzymic gravimetric and enzymic—chemical methods. This paper presents the recent developments in the extraction, . Enzymes employed had to meet specific activity requirements and be devoid of contaminating enzymes active on dietary fibre components. The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in .
This article highlights the lack of consensus on its chemical definition and the advantages and disadvantages of the two main methods used to measure it. These are the enzymic .
The main analytical problems which have been shown to influence the performance of the enzymatic-gravimetric AOAC procedures are: variable starch removal, too high final . A broad range of AOAC Official Methods of AnalysisSM (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since .In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37 degrees C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of .
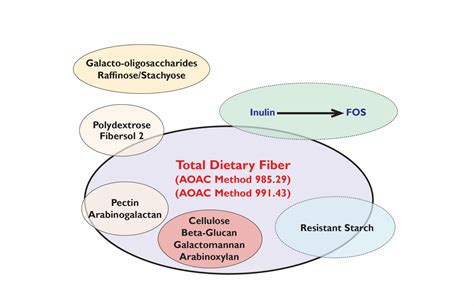
The enzymatic-chemical methods with gas-liquid chromatography (GLC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or colorimetry as endpoint determination are . A. Principle. The method measures IDF, SDF and TDF as defined by the CAC ().The method quantitates IDF and SDF which precipitates in 78% aqueous ethanol (SDFP) by gravimetric procedures, SDF which remains soluble in 78% aqueous ethanol (SDFS) by HPLC, and TDF by gravimetric and HPLC procedures (Figure 2022.01A).SDF is calculated by .
Abstract. A method for the determination of total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods. Based upon the principles of AOAC Official Methods SM 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, respectively). In 2007, McCleary .
This article highlights the lack of consensus on its chemical definition and the advantages and disadvantages of the two main methods used to measure it. These are the enzymic gravimetric method (AOAC) that measure fibre as the weight of residual matter following enzymic treatment of the food; and the enzymic chemical method that identifies and .The gravimetric method is thus regarded as a powerful tool for determining the hydrogen capacity of metal hydride/porous material and has been widely employed in this research field [20–22]. In contrast, the hydrogen uptake of porous material measured by Sieverts method has been shown to be faulty if the system volume correction is not .AOAC Official Methods SM 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, respectively). In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37 C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of HMWDF and Method 925.10 in Official Methods of Analysis, 18th Edition (AOAC International, 2007) provides an approved method for determining the moisture content of flour. A preweighed sample is heated for one hour in a 130 o C oven and transferred to a desiccator while it cools to room temperature.
Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method for estimating the quantity of a chemical correctly based on the mass of a solid.. Gravimetric analysis can be used in a variety of ways including the chemical analysis of ores and other industrial materials, equipment calibration, and elemental analysis of inorganic substances.. It is used to assess the chemical composition of rocks, .
Methods for analysis of dietary fibre
It is for these reasons that gravimetric analysis is important. Disadvantages and Limitations. Gravimetrical methods have been a traditional and widely used technique in chemical analysis; however, they come with certain disadvantages and limitations that must be considered. [7]
The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in Foods; Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method’ 4, 5. Subsequently, the method was extended to allow measurement of total, soluble and insoluble dietary fibre in foods (AOAC Official Method 991.43) 6 , and various other modified methods for fibre determination have been .DNA and Aspects of Molecular Biology. Eric T. Kool, in Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry, 1999 7.10.9.2.1 Enzymatic methods. The simplest enzymatic method for ligation of single-stranded circles is analogous to the method used for duplex DNAs. The difference here is that one uses a separate “splint” oligonucleotide to hybridize to the two reactive ends such that . This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant .
The AOAC method is an enzymatic- gravimetric procedure to determine the total dietary fibre (TDF). The Englyst method involves enzymatic-chemical extraction and fractionation of the non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) and their subsequent determination as neutral sugars by GLC. The AOAC method gave a higher fibre value than the Englyst method due .
Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method for accurately determining the amount of a substance by selective precipitation of the substance from an aqueous solution. The precipitate is separated from the remaining aqueous solution by filtration and is then weighed. Assuming that the chemical formula for the precipitate is known and that the .Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass. The principle of this type of analysis is that once an ion's mass has been determined as a unique compound, that known measurement can then be used to determine the same analyte's mass in a mixture, as long as .The disadvantages of this method are (i) . Enzymatic Methods. Analytical methods based on enzymes rely on their ability to catalyze specific reactions. These methods are rapid, highly specific and sensitive to low concentrations and are therefore ideal for determination of carbohydrates in foods. . Gravimetric Methods. Crude Fiber Method . ENZYMATIC-GRAVIMETRIC METHODS The original AOAC enzymatic-gravimetric method for the determination of total dietary fibre (TDF) was developed on basis of the joint experience of Asp et al. (1992). The origins of these methods can be tracked back to the biochemical approach of measuring the indigestible residues in human foods introduced by .
Also, methods often don't require expensive equipment. gravimetric analysis, thanks to its high degree of accuracy, when performed correctly, also can be wont to calibrate other instruments in lieu of reference standards. gravimetric analysis is currently wont to allow undergraduate chemistry/Biochemistry students to experience a grad level .A method for the determination of total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods. Based upon the principles of AOAC Official Methods 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, re .Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method Deitary Fibre in Foods AOAC 991.43 AOAC 985.29 Total Dietary Fibre in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method AOAC 993.19 Enzymatic-Gravimetric MethodSoluble Dietary Fibre in Food and Food Products. 4 AOAC 985.29 Duplicate test portions of sample Duplicate test
Using Mass as an Analytical Signal; Types of Gravimetric Methods; Conservation of Mass; Why Gravimetry is Important; Before we consider specific gravimetric methods, let’s take a moment to develop a broad survey of gravimetry.Later, as you read through the descriptions of specific gravimetric methods, this survey will help you focus on their . A general principle of gravimetric method of analysis is based on a chemical reaction between analyte and reagent. The analyte (A) of molecules ‘a’ react with the reagent (R) of molecule ‘r’. After drying, the product formed by igniting AaRr can either be weighed or ignited to create another compound of known chemical components.An analytical method is of value when its specificity, reproducibility, and sensitivity are high and when the expenditure of labor, time, and material are low. Theoretically, most of these requirements can be met admirably by enzymatic analysis (Bergmeyer 1983). The.Ask the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question gravimetric analysis, a method of quantitative chemical analysis in which the constituent sought is converted into a substance (of known composition) that can be separated from the sample and weighed. The steps commonly followed in gravimetric analysis are (1) preparation of a solution containing a known weight of .
Methodology to support this definition was separately developed by Furda (8, 9), Schweizer and Wursch (10, 11), and Asp and Johansson , leading to the enzymatic gravimetric Official Method of Analysis SM (OMA) for total DF (TDF) [Prosky et al. ; OMA 985.29] as well as for insoluble DF (IDF) and soluble DF that precipitates in 78% aqueous .Aluminum, Iron, Phosphorus, and Titanium Oxides in Liming Materials: Gravimetric Method Notes. Notes. 1.3.04 AOAC Official Method 917.02 Calcium in Liming Materials: Gravimetric Method Notes. Notes. 1.3.05 AOAC Official Method 919.01 Magnesium in Liming Materials: Gravimetric Method . Colorimetric Enzymatic Method Notes . The enzymatic-gravimetric methods AOAC 2009.01 (McCleary et al., 2010) and AOAC 2011.25 (McCleary et al., 2012) are “new” general methods that quantify most of the DF components included in the definition proposed by the Codex Alimentarius, including the LMWDF fraction. The AOAC 2009.01 method quantifies the total dietary fiber (TDF . Using Mass as an Analytical Signal; Types of Gravimetric Methods; Conservation of Mass; Why Gravimetry is Important; Before we consider specific gravimetric methods, let’s take a moment to develop a broad survey of gravimetry.Later, as you read through the descriptions of specific gravimetric methods, this survey will help you focus on their .
Measurement of Dietary Fiber: Which AOAC Official Method of
17 de set. de 2022 · Upcoming TV Airings 2018–2022 Series 3 Seasons 10 Episodes. . News about Step Up November 30, 2022 Q&A Ne-Yo Opens Up About Making Christmas Movies, Acting & Musical Longevity September 17, 2022
disadvantages of enzymatic gravimetric method|Dietary fibre in foods: a review